
What is the Key Difference Between Web2 and Web3?
- Posted by 3.0 University
- Categories Emerging Technology
- Date January 30, 2025
- Comments 0 comment
What is Web3? Indeed, an interesting question! The internet has changed how people use digital platforms and interact with one another, forming a key difference between Web2 and Web3.
As people depend more on online services, it is important for both users and developers to grasp these concepts while dealing with modern web technologies.
Web2 is known for centralized systems where users mainly access content from companies. In contrast, Web3 focuses on decentralization, promoting user ownership, privacy, and direct interactions among users.
The differences between Web2 and Web3 need to be well-understood, to be able embrace this illustrious technological development.
This piece is not merely about web3 explained in detail – but it’s more than that! This difference marks not just a change in technology but also in how we think about data control and management.
The design of each web generation is important here, as shown in, which clearly shows the move from a centralized server system to a decentralized network, highlighting the main principles that push towards Web3 and its future effects on digital interaction.
Overview of Web2 and Web3 concepts and their significance in the evolution of the internet.
The change from Web 2.0 to Web 3.0 exhibits an enormous shift in how people use digital platforms and handle their data. In the Web 2.0 model, which has centralized platforms where businesses control user-created content, individuals usually give up their personal data to get services.
This is very different from Web 3.0, which encourages decentralization, giving users more control over their data through technology like blockchain and smart contracts.
The shift from a top-down, server-based setup to a decentralized network underscores user independence.
Additionally, it points out key differences, such as ownership and data handling, showing how these aspects are crucial to Web 3.0’s promise of better privacy and security.
Therefore, understanding these ideas is important, not just for knowing technological progress but also for seeing their effects on user rights and digital interaction today.
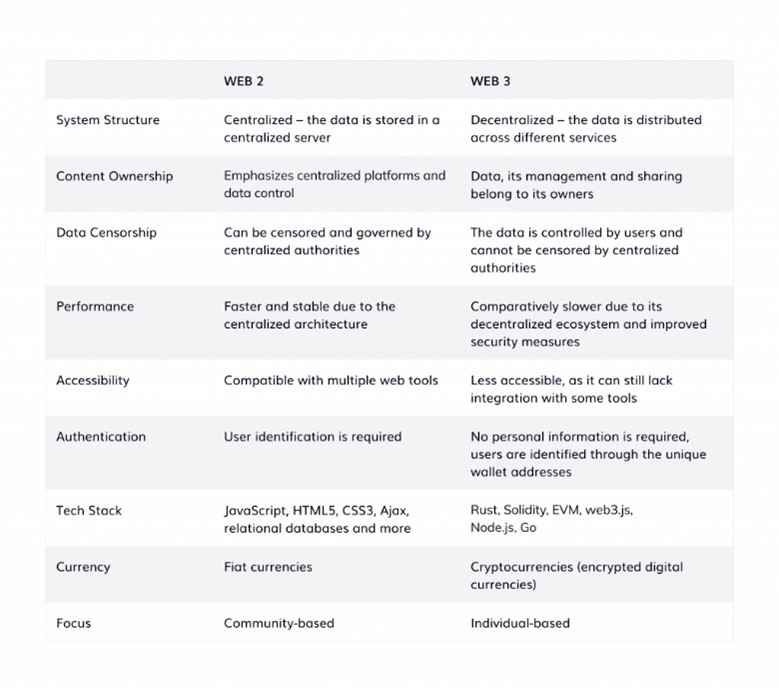
Image1. Comparison of Web 2.0 and Web 3.0 Attributes
Key Differences in Architecture
The distinctions in architecture between Web2 and Web3 are evident in their design and how users tend to engage. Web2, which is the current version of the internet, is based on centralized systems.
Users connect through platforms that control and manage how information is shared; this can be seen in social media services, as shown in the image.
Alternatively, Web3 uses decentralized systems that allow users network, without the need for any intermediary, empowering them with more control and ownership of their personal data.
This change affects data-sharing practices and improves security and transparency, with systems designed for easy auditing: Web3 represents the next step in internet development that is safer, more open, and more interactive.
These basic changes not only transform user interactions but also change how trust is built in technology, marking an important shift in digital communication.
Aspect | Web2 | Web3 |
Data Ownership | Data is owned by centralized companies. | Users have control and ownership of their own data. |
Identity Management | Identity is managed by centralized platforms (e.g., Google, Facebook). | Decentralized identity through blockchain verifies users without intermediaries. |
Monetization | Monetization primarily through advertising and subscription models. | Users can earn directly through token economies and decentralized finance (DeFi). |
Security | Centralized servers are vulnerable to hacks and data breaches. | Decentralized networks enhance security but are still susceptible to unique attacks. |
Interoperability | Limited interoperability between platforms. | Designed for greater interoperability using open protocols. |
Key Differences in Architecture Between Web2 and Web3
Here’s a Comparison of Centralized vs Decentralized systems – and their implications for user control and data ownership.
The reason for the major transformation in how not only users controls data, but also own them – which is, predominantly, key to the shift from centralized to decentralized systems.
In Web 2.0, users are mostly just data users and do not have ownership rights to their personal information.
This situation allows companies to make money from user-generated content without fairly compensating the users.
On the other hand, the decentralized structure of Web 3.0 lets users regain ownership with blockchain technology, helping them manage their data safely and transparently.
This change is very important, as decentralized systems improve privacy and give users better decision-making power about their online identities.
A useful visual aid for this change can be found in [citeX], which shows the centralized model of Web 2.0 next to the decentralized setup of Web 3.0, highlighting how much more control users have due to this new design.
This change is an important step towards an online space that values and protects user rights.
User Experience and Interaction
The move from Web2 to Web3 shows a big change in how users experience and interact with online platforms. In the Web2 model, centralized companies often control users, prioritizing profit over personal experience.
This situation can result in the misuse of data, where user privacy suffers for targeted ads.
Alternatively, in the scheme of extensity, a decentralised systems is provided by Web3 provides, which, seemingly, changes this situation, allowing users to take back control of their data and identities.
As one expert clearly puts it, Web3 aims to build a more decentralized, open, and transparent internet, giving users greater control over their data and how they interact with others.
Furthermore, decentralized apps help increase user interaction by lowering the need for middlemen, which can make processes smoother and build trust.
As a result, this new system not only changes user experiences but also sets the stage for a fairer digital future.
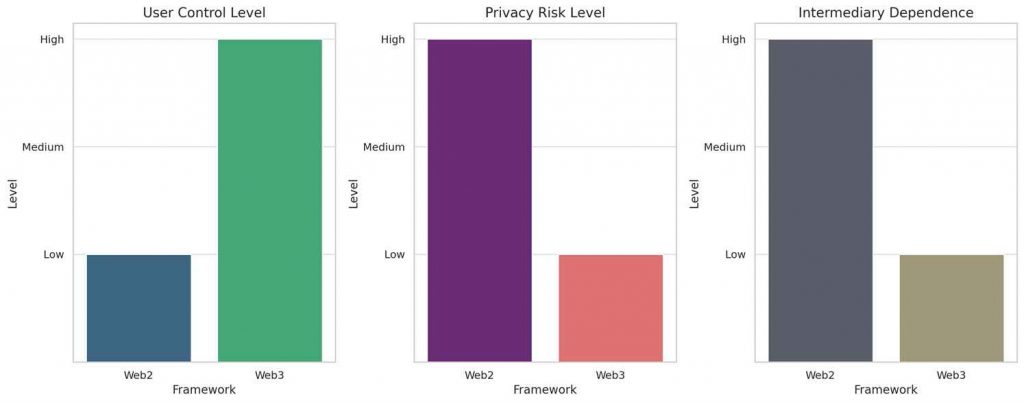
This chart compares the user control level, privacy risk level, and intermediary dependence between Web2 and Web3 frameworks.
Each bar represents the categorization of each framework in these specific areas, with Web2 showing low user control, high privacy risk, and high intermediary dependence, while Web3 offers high user control, low privacy risk, and low intermediary dependence.
Examination of how user engagement and interaction differ between Web2 platforms and Web3 applications.
A significant shift in user engagement and interaction marks the transition from Web2 to Web3. In the Web2 model, users mostly use centralized platforms, engaging through social media and apps that focus on consuming content while often using user data for profit.
This system promotes passive interaction, giving users minimal control and putting them in a setup that prioritizes retention over collaboration. On the other hand, Web3 applications empower users through decentralized systems, as seen in [citeX].
This decentralization allows for direct interactions that focus on ownership, privacy, and community involvement.
Users not only take part in their experiences but also help in making decisions and creating content, turning them into active participants rather than just consumers.
The effects of this change are significant, as interaction in Web3 promotes a feeling of independence and responsibility, setting it clearly apart from the more controlled interactions of Web2 and ultimately changing the digital world.
Conclusion
The move from Web2 to Web3 shows a big change in how people interact online, changing the way users control their data. Web2’s centralized nature often benefits companies, transforming users into consumers rather than information owners.
On the other hand, Web3 gives people more control over their data and creates a decentralized environment that helps reduce censorship and misuse.
This new structure offers more transparency and trust through technologies like blockchain and introduces new economic models based on decentralized finance and user involvement.
As shown in, the shift from a centralized system to a decentralized one highlights these major changes, suggesting that the future of the internet is not just about being connected but also about letting users take back control of their digital identities and activities.
Summary of the main distinctions and the potential future impact of Web3 on the digital landscape.
The variation or transformation from Web 2.0 to Web 3.0 demonstrates a substantial shift in how users engage with the online world, changing ideas about ownership, privacy, and how things work.
This new system moves control away from centralized services, where user data is often used for profit, to decentralized networks that allow individuals to control their information.
The rise of blockchain technology supports this change, improving transparency and security in online transactions.
This effectively highlights this structural change, showing the switch from a server-based model of Web 2.0 to a decentralized connection model in Web 3.0.
This has possible effects on many areas, like finance, governance, and media, as platforms change to focus more on user control.
As the online world keeps changing with these developments, the importance of ethical issues about data privacy and blockchain governance becomes even greater, paving the way for a fairer internet.
Learn AI, Web3, Blockchain & Cybersecurity with 3.0 University. Get certified in cutting-edge technologies and advance your career with expert-led online courses.
You may also like

Top Web3 Career Paths in 2025

Key Differences Between Ethical Hacking and Penetration Testing

