
Cybersecurity Logs: Threat Analysis, Careers & Future Scope
- Posted by 3.0 University
- Categories Cyber Security
- Date April 4, 2025
- Comments 0 comment
The Significance of Log Files in Cybersecurity
In today’s constantly changing cybersecurity landscape, system logs not only record routine details but also capture the dynamic nature of our digital world.
Log files record how apps perform, how users interact, and even when security slip-ups occur, offering a surprisingly intimate look at system operations.
Most of the time, these records provide professionals with the advantage they need to swiftly detect unauthorized access and safeguard sensitive data.
They aren’t merely lists; by continuously tracking events, logs often reveal patterns that might suggest a breach, setting the stage for prompt, proactive action.
At times, when security incidents hit, these logs piece together a timeline that guides forensic checks — a process that can be crucial to understanding what happened and why.
The growing call for log management expertise underlines just how central these files have become in strengthening our digital defenses.
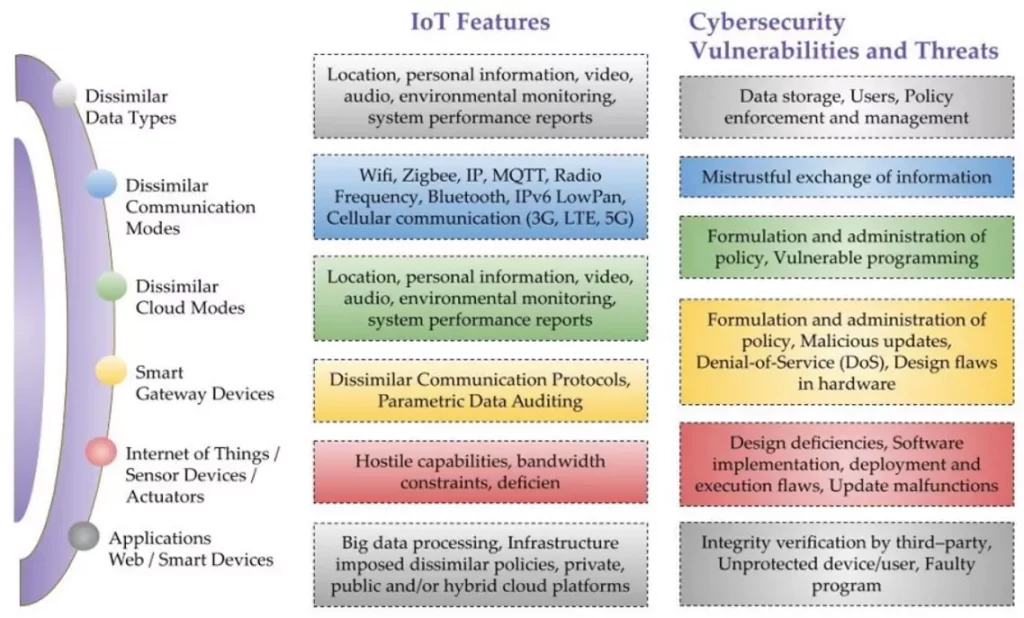
Image1. Overview of IoT Features and Cybersecurity Threats
Key Functions of Log Files in Cybersecurity
Tracking sprawling digital systems means you need a solid way to capture and sift through every activity—this is when log files step in.
Security teams lean on these records to pinpoint oddities that might hint at unauthorized break-ins or breaches; they help catch potential issues before they blow up.
With continuous monitoring, teams start noticing when things just don’t add up, which helps keep important data safe. If there’s a possible flaw or gaffe, these logs get modified into an event diary – which is a chronological record – and for the most part, it’s key for forensic digs – and reveals, in its own way, the tricks of cyber attackers.
Remember, logs aren’t just dry reports; they’re detailed text records of what happens within an organization’s IT setup, offering an audit trail that’s essential for both clarity and compliance.
In most cases, solid log management jives with regulatory requirements, smoothing out audits by showing that the organization sticks to cybersecurity standards.
All in all, weaving these files into the overall system fortifies the security scene against ever-changing threats.
Function | Description |
Monitoring and Detection | Log files record system and network activities, enabling the identification of security incidents such as unauthorized access attempts and malware infections. They provide real-time alerts and historical data for threat detection and analysis. |
Incident Response and Recovery | Logs offer detailed records of events leading up to and following a security incident, assisting in understanding the attack vector, scope, and impact. This information is crucial for effective incident response and recovery planning. |
Compliance and Auditing | Maintaining comprehensive logs is essential for meeting regulatory requirements and conducting audits. Logs provide evidence of security controls and activities, supporting compliance with standards like FISMA and HIPAA. |
System Performance Monitoring | Logs capture system performance metrics, helping in identifying bottlenecks, resource utilization issues, and potential vulnerabilities. Regular analysis aids in optimizing system performance and reliability. |
Forensic Analysis | In the event of a security breach, logs serve as a critical source of information for forensic investigations, helping to reconstruct events, determine the cause, and develop strategies to prevent future incidents. |
Key Functions of Log Files in Cybersecurity
Emerging Job Roles in Log Management and Analysis
Today, the role of log files in cybersecurity has evolved from being mere records to serving as early warning indicators against hidden threats.
Many organizations now lean on tough cyber defenses, calling on experts like Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) specialists and cybersecurity analysts to work with these logs in unexpected, hands-on ways.
In most cases, these roles demand a real knack for handling log data: professionals here manage security incidents, spot vulnerabilities, and set up measures to deter breaches, which clearly shows the growing need for savvy expertise.
For instance, Incident Response Analysts are becoming increasingly important as they delve into logs to address incidents immediately and subsequently conduct more thorough forensic checks.
These positions also help companies keep on the right side of legal rules—avoiding penalties while boosting stakeholder trust.
Aligned with it, this shift suggests that mastering log management fills a notable talent gap and opens up a wide range of career opportunities, hinting at a promising pathway for future growth in the cybersecurity arena.
Job Role | Median Annual Wage (2022) | Projected Employment Growth (2022–2032) | Annual Openings (2022–2032) |
Information Security Analyst | $112,000 | 31.5% | 16,800 |
Software Developer | $127,260 | 25.7% | 136,300 |
Computer and Information Research Scientist | $136,620 | 22.7% | 3,400 |
Software Quality Assurance Analyst and Tester | $99,620 | 20.3% | 17,500 |
Web Developer | $78,580 | 17.0% | 8,300 |
Web and Digital Interface Designer | $83,240 | 15.2% | 10,700 |
Database Architect | $134,870 | 10.0% | 4,500 |
Emerging Job Roles in Log Management and Analysis within Cybersecurity
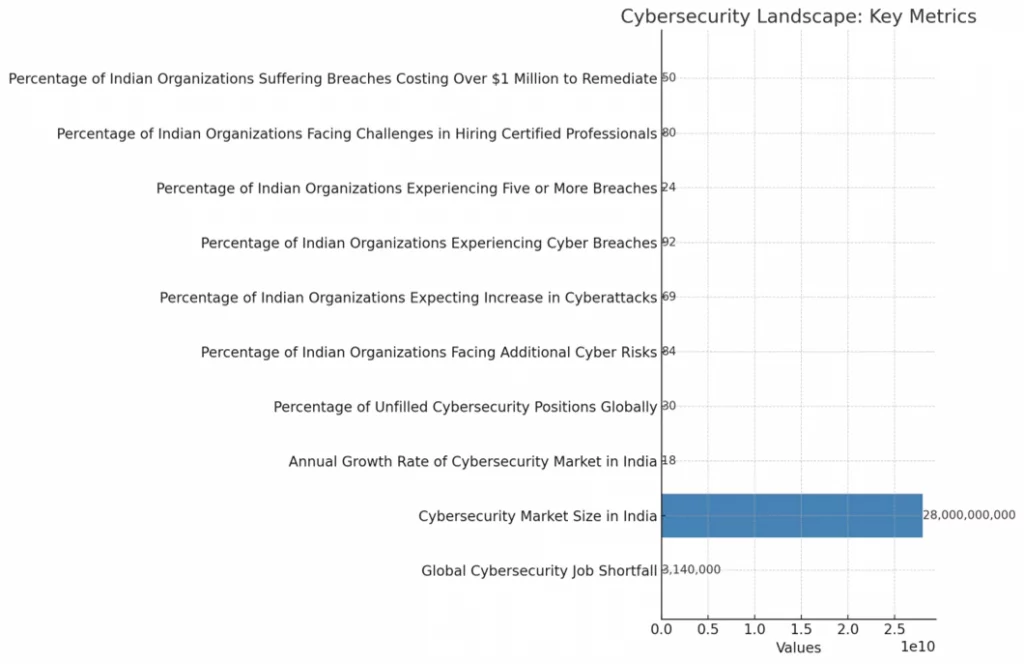
This bar chart demonstrates key metrics – they are related to cybersecurity, and includes the global job deficit in cybersecurity professionals, apart from the size of the cybersecurity market in India, and various challenges faced by Indian organizations such as unfilled positions and increasing cyber risks. Each metric is conspicuously labelled, and the values are presented to highlight the significance of these issues within the cybersecurity landscape.
Region | Cybersecurity Professionals Needed by 2025 | Current Cybersecurity Professionals (2019) | Growth Percentage | Source | |||||||
India | 64,000 | 110,000 | 58.18% | Data Security Council of India (DSCI) | |||||||
India | 5,00,000 to 12,00,000 | 5,00,000 to 10,00,000 | 10,00,000 to 25,00,000 | 15,00,000 to 30,00,000 | 12,00,000 to 25,00,000 | 6,00,000 to 15,00,000 | 5,00,000 to 12,00,000 | 8,00,000 to 18,00,000 | 25,00,000 to 50,00,000 | 8,00,000 to 20,00,000 | Takshashila University |
India | 64,000 | 110,000 | 58.18% | Data Security Council of India (DSCI) | |||||||
Worldwide | 3.5 million | 2.7 million | 77% | Cybersecurity Ventures |
Cybersecurity Job Market Outlook in India and Worldwide
Conclusion
It won’t be amiss if it’s said that Digital systems are omnipresent now, and what’s imperative – the answer is, perpetually, comprehending cybersecurity is a must, now—especially when it comes to keeping track of your logs.
Log files serve more than just displaying system behavior; they serve as the primary tool for identifying potential threats and managing incidents, thereby preventing sensitive data from falling into the wrong hands.
The world is, evidently, changing rapidly, and for sure, there is a rising interest in career opportunities.
The latest projections predict approximately 3.5 million unfilled positions, by 2025, which, most certainly, demonstrates the significant demand for skilled individuals.
This gap, in most cases, highlights the urgent call for experts, like those working as cybersecurity analysts and SIEM specialists.
Looking at detailed frameworks in images like this, you can see that solid preparation really matters for anyone aiming to leave a mark in cybersecurity.
As the image clearly illustrates, comprehending log files not only demonstrate technical proficiency but also serves as a crucial tool for unlocking numerous future career opportunities.
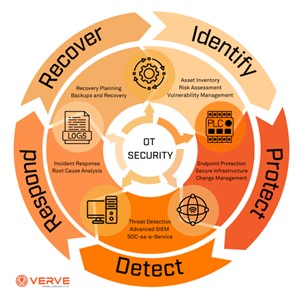
Image2. Framework for Operational Technology Security Management
You may also like

Firewalls & Future of Cybersecurity Careers in 2025

What are Logs in Cybersecurity?

