Blockchain vs Traditional Databases: Which is Better?
- Posted by 3.0 University
- Categories Blockchain
- Date January 13, 2025
- Comments 0 comment
In a time when digital information influences decisions and business, how we manage data is being questioned. Traditional databases, like well-organized filing cabinets, provide structured access but have limits, including single points of failure and risk of tampering. Is it just about Blockchain vs database, Or more?
On the other hand, blockchain technology stands out as a new kind of ledger, not vulnerable to these issues because of its decentralized and unchangeable design. The analogy of a strong barrier surrounding a secure vault effectively illustrates blockchain technology’s enhanced data integrity and transparency.
While traditional databases can handle large amounts of data well, they often miss the strong verification features of blockchain, making it a better option for uses that need strong trust and accountability.
As the digital world changes, it is important to understand the differences and benefits of these systems, raising the essential question: Which system is more appropriate for addressing the challenges of modern data management?

Overview of Blockchain and Traditional Databases
Beyond just Blockchain advantages over databases, what’s more important is – in the area of data management and complex tech systems, looking at blockchain and traditional databases shows key differences in how they are built and how they work.
Traditional databases usually sit in one place and use a client-server setup, which gives one group control over who can see and use the data, leading to worries about security and trustworthiness.
On the other hand, blockchain uses a decentralized approach where everyone in the network has a copy of the ledger, which encourages openness and builds trust among users. Since everyone in the network must agree to change one entry, this setup reduces the likelihood of data alteration.
What thwarts Traditional database limitations is that traditional databases can be efficient for specific uses, but they can face issues with scalability and risk having a single point of failure.
As organizations look for more reliable and accountable options, knowing these differences is important to decide which choice—blockchain or traditional databases—fits their changing needs best. The discussion will look deeper at these points.
Database Type | Data Structure | Scalability | Security | Transaction Speed | Use Cases |
Blockchain | Distributed ledger with immutable records | Limited scalability due to consensus mechanisms | High security through cryptographic techniques | Slower transaction speed due to decentralized verification | Cryptocurrencies, supply chain management, smart contracts |
Traditional Database | Centralized or distributed relational structures | Higher scalability options with vertical and horizontal scaling | Vulnerable to central points of failure; security measures depend on implementation | Faster transaction speed with immediate consistency | Enterprise applications, online transactions, data analytics |
Comparison of Blockchain and Traditional Databases
Advantages of Blockchain Technology
In the data-focused world today, there is a significant need for systems that provide strong security, clear visibility, and high efficiency. Blockchain technology stands out as a strong option, with clear benefits over regular databases.
Unlike traditional systems that depend on central authorities, blockchain uses a decentralized setup, spreading data across many nodes in a network.
This decentralization helps reduce risks linked to single failures while also improving data accuracy by using cryptographic methods for securing transactions.
In addition, the natural openness of blockchain builds trust among users since all parties can confirm and review transactions as they happen.
This level of transparency is especially important in areas like environmental management, where “blockchain technology can provide new ways to measure and track emissions reductions more accurately, allowing us to create more effective carbon offset projects.”
Overall, these benefits make blockchain a game-changing tool that changes how data is handled and shared in different fields.
Enhanced Security and Transparency
In data management, the need for security and transparency is very clear. Traditional databases, which are often centralized and depend on one entity to maintain data integrity, leave companies vulnerable to issues like unauthorized access and data breaches.
Conversely, blockchain technology functions as a robust digital barrier. It records each transaction in unchangeable blocks that all network participants can see. This decentralized setup reduces the chances of data tampering and encourages trust among users, as every action can be seen and confirmed.
For example, in supply chain management, blockchain improves traceability and lets stakeholders easily follow a product’s journey from its source to the consumer.
In the end, moving from traditional databases to blockchain marks an important advance; better security and transparency are key parts of a more sturdy and dependable data system, changing how we view data integrity.
Limitations of Traditional Databases
In a world that is more connected, the problems in traditional databases are very clear. The centralized setup of these systems creates big security risks; as noted, “a traditional database has a centralized structure.
This means the data is stored in one central location under the control of a single entity that determines how new data is added to the database, modified, or removed.”
This design not only causes delays in data management but also makes it an accessible target for cyberattacks, where a hacked administrator can put sensitive data at risk.
Additionally, depending on one entity for data control often results in a lack of transparency and trust, making it challenging for stakeholders to work together.
The rigidity of traditional databases also limits their ability to adapt to changing data management needs, causing problems for organizations aiming to innovate.
On the other hand, blockchain technology offers a major change, reducing these issues through decentralization and better security measures.
Vulnerabilities and Centralization Issues
In a connected digital world, traditional databases have vulnerabilities like cracks in a strong wall; they might not be seen, but their effects can be very serious. Centralization is a big problem, as traditional databases usually depend on one entity to handle data, making them simple targets for cyberattacks.
This single failure point weakens the integrity, availability, and confidentiality of data, leaving organizations open to breaches that can have extensive effects.
In contrast, blockchain technology uses a decentralized system that spreads data across many nodes, greatly lowering the risks from breaches.
This setup builds trust among users and strengthens the network against harmful actions.
By overcoming the shortcomings of traditional databases, blockchain becomes a stronger option, meeting the urgent need for secure data management in today’s digital world.
The seriousness of these vulnerabilities highlights the strong case for using blockchain technology instead of traditional systems.
Conclusion
In the end, the rise of blockchain as a new technology brings both challenges and chances for old database systems.
By looking at the benefits of blockchain—like being decentralized, better security, and greater transparency—compared to the downsides of traditional databases, we can see how data management is changing.
Old databases usually work as centralized storage points that can be targeted for data breaches and corruption, similar to one weak point in a big machine that can make the whole thing fail if it breaks.
On the other hand, blockchain acts like a strong web where each part supports the others, keeping trust and integrity through cryptographic checks.
As businesses look for ways to improve security and efficiency, the choice of which system to use depends on their specific needs and resources.
Therefore, while both have benefits, the future of data management is likely to favor blockchain because it’s crucial to protect information in a more digital world.
Comparative Analysis and Future Implications
As organizations deal with data management issues, the difference between blockchain technology and traditional databases becomes an important factor for future infrastructure choices.
Traditional databases work on centralized systems, which can make them prone to single points of failure, while blockchain provides a decentralized structure that improves security and transparency.
This change is not just theory; it has real impacts on many sectors such as finance, healthcare, and supply chain management. Blockchain’s features, like immutability and consensus processes, offer important benefits, especially in areas where data integrity matters a lot.
On the other hand, the limitations of traditional databases, like scalability and risk of data breaches, highlight how blockchain could transform how organizations exchange and manage information.
In this changing environment, using blockchain technology may redefine standards for data management, leading to a need to rethink outdated systems that might block future progress.
Empower your career with 3.0 University next-gen online courses in Web3 technologies.
Explore the AI-Powered Ethical Hacking Program, dive into advanced cybersecurity, and master Blockchain and AI innovations—all with global certifications.
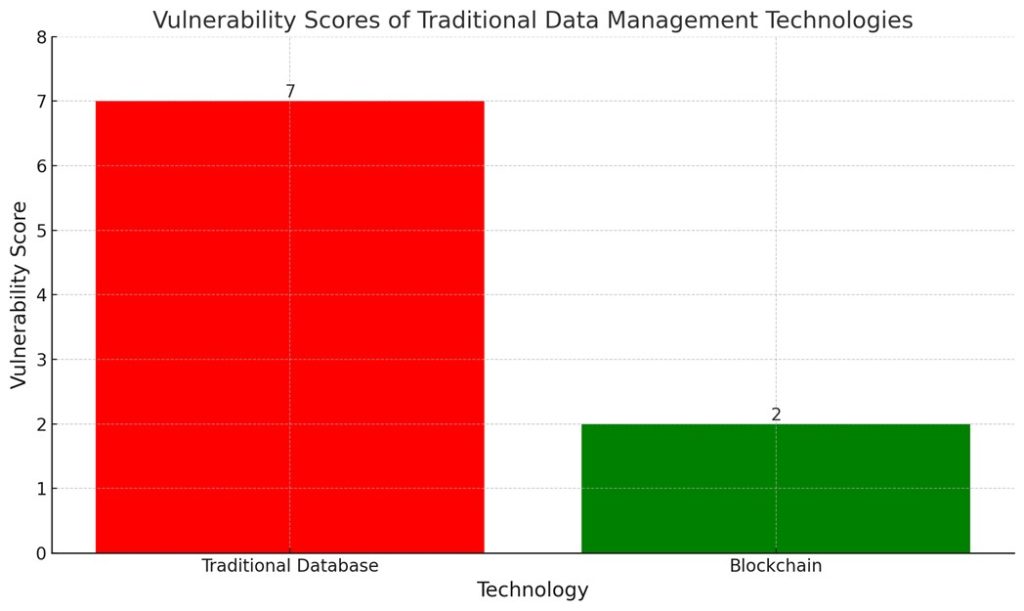
The chart displays the vulnerability scores of two different technologies: Traditional Database and Blockchain. It visually compares the higher vulnerability associated with Traditional Databases to the significantly lower vulnerability score attributed to Blockchain technology.
You may also like

Blockchain and Crypto Education Boom in India

Career Opportunities in Blockchain for 2025

